Since the late 1970’s in the face of a severe loss of market share in dozens of industries, manufacturers in the United States have been trying to improve productivity—and therefore enhance their international competitiveness—through cost-cutting programs. (Cost-cutting here is defined as raising labor output while holding the amount of labor constant.) However, from 1978 through 1982, productivity—the value of goods manufactured divided by the amount of labor input—did not improve; and while the results were better in the business upturn of the three years following, they ran 25percent lower than productivity improvements during earlier, post-1945 upturns. At the same time, it became clear that the harder manufactures worked to implement cost-cutting, the more they lost their competitive edge.
With this paradox in mind, I recently visited 25 companies; it became clear to me that the cost-cutting approach to increasing productivity is fundamentally flawed. Manufacturing regularly observes a “40, 40, 20” rule. Roughly 40 percent of any manufacturing-based competitive advantage derives from long-term changes in manufacturing structure (decisions about the number, size, location, and capacity of facilities) and in approaches to materials. Another 40 percent comes from major changes in equipment and process technology. The final 20 percent rests on implementing conventional cost-cutting. This rule does not imply that cost-cutting should not be tried. The well-known tools of this approach—including simplifying jobs and retraining employees to work smarter, not harder—do produce results. But the tools quickly reach the limits of what they can contribute.
Another problem is that the cost-cutting approach hinders innovation and discourages creative people. As Abernathy’s study of automobile manufacturers has shown, an industry can easily become prisoner of its own investments in cost-cutting techniques, reducing its ability to develop new products. And managers under pressure to maximize cost-cutting will resist innovation because they know that more fundamental changes in processes or systems will wreak havoc with the results on which they are measured. Production managers have always seen their job as one of minimizing costs and maximizing output. This dimension of performance has until recently sufficed as a basis of evaluation, but it has created a penny-pinching, mechanistic culture in most factories that has kept away creative managers.
Every company I know that has freed itself from the paradox has done so, in part, by developing and implementing a manufacturing strategy. Such a strategy focuses on the manufacturing structure and on equipment and process technology. In one company a manufacturing strategy that allowed different areas of the factory to specialize in different markets replaced the conventional cost-cutting approach; within three years the company regained its competitive advantage. Together with such strategies, successful companies are also encouraging managers to focus on a wider set of objectives besides cutting costs. There is hope for manufacturing, but it dearly rests oil a different way of managing.
The author refers to Abernathy’s study most probably in order to _____.
“As Abernathy’s study of automobile manufacturers has shown, an industry can easily become prisoner of its own investments in cost-cutting techniques, reducing its ability to develop new products.”提到Abernathy的研究主要是否定cost-cutting,从而肯定新方法对于提高生产力的帮助。
鉴别再生障碍性贫血和白细胞减少型白血病的主要检查是
男性,24岁。头痛、头晕1个月,高热、鼻出血1周,浅表淋巴结不大,肝可及边,脾未及,血象检查:红细胞1.8×10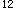 /L,血小板20×10
/L,血小板20×10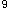 /L,WBC1.5×10
/L,WBC1.5×10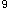 /L骨髓象红系和粒系各阶段比例大致正常,但未见巨核细胞。最可能的诊断应考虑为
/L骨髓象红系和粒系各阶段比例大致正常,但未见巨核细胞。最可能的诊断应考虑为
女性,20岁。因泌尿系感染,一年来反复应用多种抗生素治疗,近一周来发热,全身皮肤及口腔粘膜出血,血红蛋白下降至60g/L,白细胞2.5×10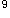 /L,血小板30×10
/L,血小板30×10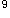 /L,网织红细胞0.2%,骨髓增生为极度减低,应诊断为
/L,网织红细胞0.2%,骨髓增生为极度减低,应诊断为
典型再障的骨髓象重要标志是
下列哪种贫血,外周血片中不会出现幼红细胞
再生障碍性贫血应与下列哪种疾病鉴别
再生障碍危象早期骨髓检查的特征是
单纯红细胞再生障碍性贫血时可见
急性再生障碍性贫血的骨髓增生程度大多呈
再生障碍性贫血与下列哪些关系不显著