Passage 1
Economically speaking,are we better off than we were ten years ago Twenty years ago
In their thirst for evidence on this issue,commentators seized on the recent report by the Census Bureau,which found that average household income rose by 5.2%in 2014.Unfortunately,that conclusion puts too much weight on a useful,but flawed and incomplete,statistic.Among the more significant problems with the Census's measure are that:1)it excludes taxes,transfers,and compensation like employer-provided health insurance;and 2)it is based on surveys rather than data.Even if precisely measured,income data exclude important determinants of economic well-being,such as the hours of work needed to earn that income.
While thinking about the question,we came across a recently published article by Charles Jones and Peter Klenow,which proposes an interesting new measure of economic welfare.While by no means perfect,it is considerably more comprehensive than average income,taking into account not only growth in consumption per person but also changes in working time,life expectancy,and inequality.Moreover,it can be used to assess economic performance both across countries and over time.
The Jones-Klenow method can be illustrated by a cross-country example.Suppose we want to compare the economic welfare of citizens of the U.S.and France in 2005.
In 2005,as the authors observe:real consumption per person in France was only 60%as high as the U.S.,making it appear that Americans were economically much better off than the French on average.However,that comparison omits other relevant factors:leisure time,life expectancy,and economic inequality.The French take longer vacations and retire earlier,so typically work fewer hours;they enjoy a higher life expectancy,presumably reflecting advantages with respect to health care,diet,lifestyle,and the like;and income and consumption are somewhat more equally distributed there than in the U.S.Because of these differences,comparing France's consumption with the U.S.'s overstates the gap in economic welfare.
Similar calculations can be used to compare the U.S.and other countries.For example,this calculation puts economic welfare in the United Kingdom at 97%of U.S.levels,but estimates Mexican well-being at 22%.
The Jones-Klenow measure can also assess an economy's performance over time.According to this measure,as of the early-to-mid-2000s,the U.S.had the highest economic welfare of any large country.Since 2007,economic welfare in the U.S.has continued to improve.However,the pace of improvement has slowed markedly.
Methodologically,the lesson from the Jones-Klenow research is that economic welfare is multi-dimensional.Their approach is flexible enough that in principle other important quality-of-life changes could be incorporated-for example,decreases in total emissions of pollutants and declines in crime rates.
What do Jones and Klenow think of the comparison between France and the U.S.in terms of real consumption per person ( )
根据题干关键词France and US定位至第四段和第五段,However,that comparison omits other relevant factors:leisure time,life expectancy,and economic inequality.然而,这种比较忽略了其他相关因素:闲暇时间、预期寿命和经济不平等。很明显,B项中neglected和important indicators分别与该句中omits和relevant factors对应。A项明显与文章主旨不符,而D项中美、法两国在自然资源方面的差异文中根本没有提到,可以排除,C相中有很大的迷惑性,国民个人之间的差异比较含糊,到底指的是美、法两国公民之间的个体差异还是两个国家内部公民之间的个体差异或两者兼而有之 相比较而言,B项意思更为明确,而且该选项中的相关表述与对应的阅读点之间存在明显的对应关系。故本题正确答案选B。
根据《中华人民共和国中国人民银行法》的规定,我国货币政策的最终目标是( ),并以此促进经济增长。
箱子里面有红、白两种玻璃球,红球数比白球数的3倍多两个,每次从箱子里取出7个白球、15个红球。如果经过若干次以后,箱子里只剩下3个白球、53个红球,那么,箱子里原有红球比白球多多少个?
将自然数1~100分别写在完全相同的100张卡片上,然后打乱卡片,先后随机取出4张,问这4张先后取出的卡片上的数字呈增序的几率是多少?()

对于债券利率的风险结构,描述正确的有( )。
市场经济体制下,财政具有的职能有( )。
( )决定着生产关系。
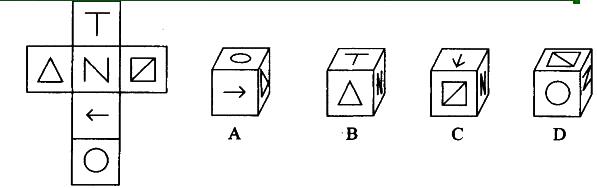
左边给定的是纸盒的外表面,下列哪一项能由它折叠而成?( )
货币制度最基本的内容是规定( )。
如果一国货币汇率上升,即对外升值,就可能会导致( )。
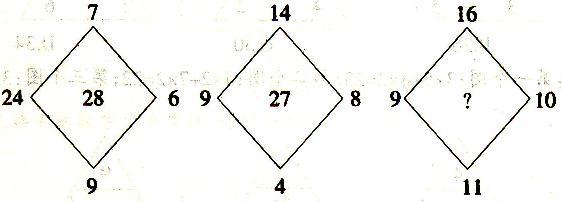
()