Passage 5
Desertification,drought,and despair-that is what global warming has in store for much of Africa.Or so we hear.
Emerging evidence is painting a very different scenario,one in which rising temperatures could benefit millions of Africans in the driest parts of the continent.Scientists are now seeing signals that the Sahara desert and surrounding regions are greening due to increasing rainfall.If sustained,these rains could revitalize drought-ravaged regions,reclaiming them for farming communities.This desert-shrinking trend is supported by climate models,which predict are turn to conditions that turned the Sahara into a lush plain some 12,000 years ago.
The green shoots of recovery are showing up on satellite images of regions including the Sahel,a semi-desert zone bordering the Sahara to the south that stretches some 2,400 miles.
Images taken between 1982 and 2002 revealed extensive re-greening throughout the Sahel,according to a new study in the journal Biogeo sciences.The study suggests huge increases in vegetation in areas including central Chad and western Sudan.The transition may be occurring because hotter air has more capacity to hold moisture,which in turn creates more rain,said Martin Claussen of the Max Planck Institute for Meteorology in Hamburg,Germany.“The water-holding capacity of the air is the main driving force.”Claussen said.
While satellite images can’t distinguish temporary plants like grasses that come and go with the rains,ground surveys suggest recent vegetation change is firmly rooted.In the eastern Sahara area of southwestern Egypt and northern Sudan,new trees are flourishing,according to Stefan Kropelin,a climate scientist at the University of Cologne’s Africa Research Unit in Germany.
“Before,there was not a single scorpion,not a single blade of grass,”said Kropelin,who has studied the region for two decades.“Now you have people grazing their camels in areas which may not have been used for hundreds or even thousands of years.You see birds,ostriches,coming back,even sorts of amphibians coming back,”he said.“The trend has continued for more than 20 years.It is indisputable.”
An explosion in plant growth has been predicted by some climate models.For instance,in 2005 a team led by Reindert Haarsma of the Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute in De Bilt,the Netherlands,forecast significantly more future rainfall in the Sahel.The study in Geophysical Research Letters predicted that rainfall in the July to September wet season would rise by up to two millimeters a day,by2080.
Satellite data shows“that indeed during the last decade,the Sahel is becoming greener,”Haarsma said.Even so,climate scientists do not agree on how future climate change will affect the Sahel—some studies simulate a decrease in rainfall.“This issue is still rather uncertain,”Haarsma said.
Max Planck’s Claussen said North Africa is the area of greatest disagreement among climate change modelers.Forecasting how global warming will affect the region is complicated by its vast size and the unpredictable influence of high-altitude winds that disperse monsoon rains,Claussen added.“Half the models follow a wetter trend,and half a drier trend.”
What?are?the?climate?scientists’attitudes?towards?the?influence?of?climate?change?on?the?deserted?areas?( )
A项:肯定的、一定的;B项:半信半疑的;C项:严肃的;D项:消极的。根据题干关键词climate scientists定位至倒数第二段,climate scientists do not agree on how future climate change will affect the Sahel—some studies simulate a decrease in rainfall.“This issue is still rather uncertain,”气候科学家对未来气候变化将如何影响萨赫勒地区仍有分歧,也就是说,这个问题仍然相当不确定。故本题正确答案选B。
根据《中华人民共和国中国人民银行法》的规定,我国货币政策的最终目标是( ),并以此促进经济增长。
箱子里面有红、白两种玻璃球,红球数比白球数的3倍多两个,每次从箱子里取出7个白球、15个红球。如果经过若干次以后,箱子里只剩下3个白球、53个红球,那么,箱子里原有红球比白球多多少个?
将自然数1~100分别写在完全相同的100张卡片上,然后打乱卡片,先后随机取出4张,问这4张先后取出的卡片上的数字呈增序的几率是多少?()

对于债券利率的风险结构,描述正确的有( )。
市场经济体制下,财政具有的职能有( )。
( )决定着生产关系。
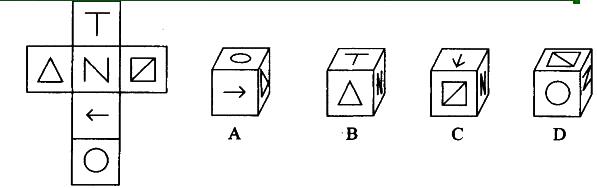
左边给定的是纸盒的外表面,下列哪一项能由它折叠而成?( )
货币制度最基本的内容是规定( )。
如果一国货币汇率上升,即对外升值,就可能会导致( )。
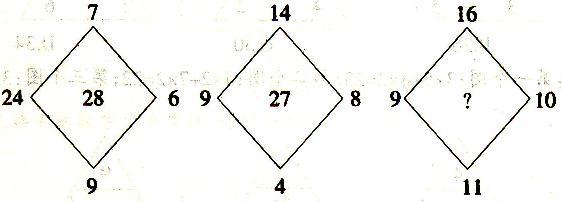
()