()既具有检错功能又具有纠错功能
奇偶校验码是最简单的检错码,奇/偶校验码包括水平奇/偶校验码、垂直奇/偶校验码和水平垂直奇/偶校验码三种编码。由于实现起来比较容易而被广泛采用。
海明码是一种可以纠正一位差错的编码。它是利用在信息位为k位,增加r位冗余位,构成一个n=k+r位的码字,然后用r个监督关系式产生的r个校正因子来区分无错和在码字中的n个不同位置的一位错。它必需满足以下关系式:
2r>=n+1 或 2r>=k+r+1
循环冗余校验:数据通信中应用最广的一种检验差错方法。方法是在发送端用数学方法产生一个循环码,叫做循环冗余检验码。在信息码位之后随信息一起发出。在接收端也用同样方法产生一个循环冗余校验码。将这两个校验码进行比较,如果一致就证明所传信息无误;如果不一致就表明传输中有差错,并要求发送端再传输。
The metric assigned to each network depends on the type of protocol. Some simple protocol, like RIP, treats each network as equals. The( )of passing through each network is the same; it is one( )count. So if a packet passes through 10 network to reach the destination, the total cost is 10 hop counts. Other protocols, such as OSPF, allow the administrator to assign a cost for passing through a network based on the type of service required. A( )through a network can have different costs (metrics). For example, if maximum( )is the desired type of service, a satellite link has a lower metric than a fiber-optic line. On the other hand, if minimum( )is the desired type of service, a fiber-optic line has a lower metric than a satellite line. OSPF allow each router to have several routing table based on the required type of service.
问题1选项
A.number
B.connection
C.diagram
D.cost
问题2选项
A.process
B.hop
C.route
D.flow
问题3选项
A.flow
B.window
C.route
D.cost
问题4选项
A.packet
B.throughput
C.error
D.number
问题5选项
A.delay
B.stream
C.packet
D.cost
在SNMP中,管理进程查询代理中一个或多个变量的值所用报文名称为( ),该报文的缺省目标端口是( )。
问题1选项
A.get-request
B.set-request
C.get-response
D.trap
问题2选项
A.160
B.161
C.162
D.163
报文摘要算法MD5的输出是( )位,SHA-1的输出是( )位。
问题1选项
A.56
B.128
C.160
D.168
问题2选项
A.56
B.128
C.160
D.168
网络由6个路由器互连而成,路由器之间的链路费用如下图所示,从PC机到服务器的最短路径是( ),通路费用是( )。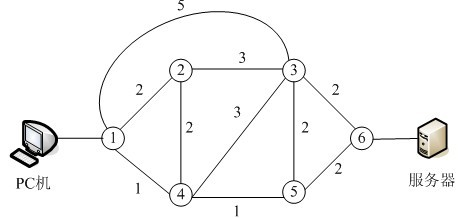
问题1选项
A.1→3→6
B.1→4→5→6
C.1→4→3→6
D.1→2→4→5→6
问题2选项
A.4
B.5
C.2
D.6
通过ADSL访问Internet,在用户端通过( )和ADSL Modem连接PC机,在ISP端通过( )设备连接因特网。
问题1选项
A.分离器
B.电话交换机
C.DSLAM
D.IP路由器
问题2选项
A.分离器
B.电话交换机
C.DSLAM
D.IP路由器
利用SDH实现广域网互联,如果用户需要的数据传输速率较小,可以用准同步数字系列(PDH)兼容的传输方式在每个STM-1帧中封装( )个E1信道。
网络系统设计过程中,逻辑网络设计阶段的任务是( )。
大型局域网通常划分为核心层、汇聚层和接入层,以下关于各个网络层次的描述中,不正确的是( )。
网络系统生命周期可以划分为5个阶段,实施这5个阶段的合理顺序是( )。
2009年发布的( )标准可以将WLAN的传输速率由54Mb/s提高到300~600Mb/s。