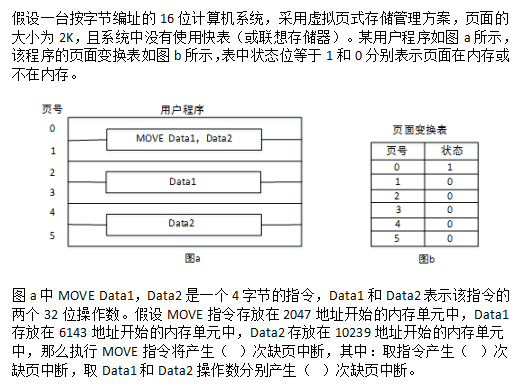
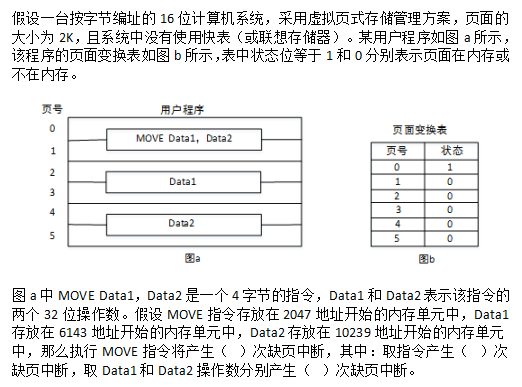
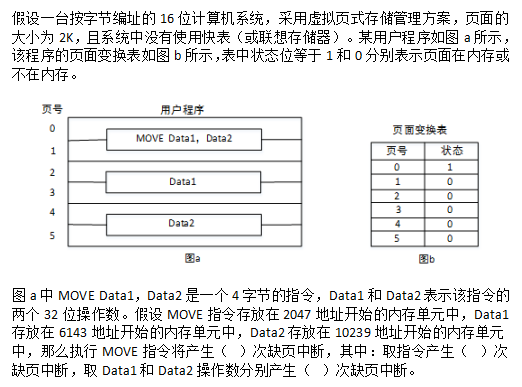
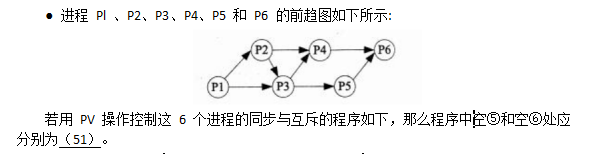
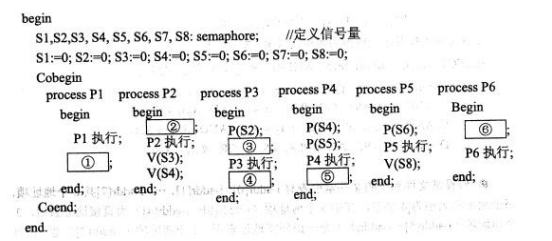
阅读以下说明和C程序,将应填入(n)处的字句写在对应栏内。
【说明】
下面的程序按照以下规则输出给定名词的复数形式。
a.若名词以“y”结尾,则删除y并添加“ies”;
b.若名词以“s”、“ch”或“sh”结尾,则添加“es”;
c.其他所有情况,直接添加“s”。
【C程序】
include <stdio.h>
include <string.h>
char*plural(char *word)
{
int n;
char *pstr;
n=strlen(word); /*求给定单词的长度*/
pstr=(char*)malloc(n+3);/*申请给定单词的复数形式存储空间*/
if (!pstr||n<2)
return NULL;
strcpy(pstr,word); /*复制给定单词*/
if ((1))
{
pstr[n-1]='i';pstr[n] ='e';pstr[n+1]='s';(2);
}
else
if(pstr[n-1]=='s'| |pstr[n-1]=='h'&&((3)))
{
pstr[n]='e';pstr[n+1]='s';pstr[n+2]='/0';
}
else
{ pstr[n]='s';pstr[n+1]='/0';)
(4);
}
main()
{ int i; char *ps;
char wc[9][10]=
{'chair','dairy','boss','circus','fly','dog','church','clue','dish');
for(i = 0;i<9; i++) {
ps= (5) ;
printf('%s: %s/n',wc[i],ps); /*输出单词及其复数形式*/
free(ps); /*释放空间*/
}
system('pause');
}
(1)pstr[n-1]='y',或*(pstr+n-1)=='y',或其等价表示 (2)pstr[n+2]='\0',或*(pstr+n+2)='\0',或其等价表示 (3)pstr[n-2]='c'||pstr[n-2]='s',或其等价表示 (4)return pstr (5)plural(wc[i]),或其等价表示
【解析】
本题考查C程序设计基本能力和字符串处理基本操作。 C程序中字符串存储在字符数组中,串的结尾需要设置结束标志符号'\0'。若已知串 pstr的长度为n(不包括结束标志),则串中的字符依次存储在pstr[0],pstr[1],...,pstr[n-1]中。因此,名词的最后一个字符pstr[n-1]若等于字符“y”,则按照规则a求其复数形式。下面的if语句处理的是以“y”结尾的名词,因此,空(1)处应填入“pstr[n-1]='y'”或其等价形式。由于串pstr的长度发生了变化,所以需要设置新的结束标志,空(2)处应填入“pstr[n+2]='\0'”’或其等价形式。
if( (1) )
{
pstr[n-1]= 'I'; pstr[n]= 'e'; pstr[n+1] = 's'; (2) ;
}
显然,下面的if语句处理规则b所示的情况,即串的末尾为“s”、“ch”或“sh”的情形,空(3)处应填入“pstr[n-2]='c'||pstr[n-2]='s”或其等价形式。
if(pstr[n-1]=='s'||pstr[n-1]=='h' && ( (3) ))
{
pstr[n] = 'e'; pstr[n+1] ='s'; pstr[n+2]='\0';
}
根据函数“char *plural(char *word)”的定义,最后应将求得的给定名词的复数形式返回给主调函数mae,对于串,应返回串空间的首地址,即返回指针pstr,因此空(4)处应填入“return pstr”。
根据以下代码,空(5)处应调用函数plural(char*word)对指定名词求复数,数组 WC初始化时已设置了名词序列,因此,空(5)处应填入“plural(wc[i])”。
for(i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
ps= (5) ;
printf("%s: %s\n",wc[i],ps); /*输出单词及其复数形式*/
free(ps);
/*释放空间*/
}