Software entities are more complex for their size than perhaps any other humanconstruct, because no two parts are alike (at least above the statement level).If they are, we make the two similar parts into one, a (), open or closed.In this respect softwaresystems differ profoundly from computers, buildings, or automobiles, where repeatedelements abound.
Digital computers are themselves more complex than most things people build; theyhave very large numbers of states.This makes conceiving, describing, and testing them hard.Software systems have orders of magnitude more()than computers do.
Likewise, a scaling-up of a software entity is not merely a repetition of the sameelements in larger size; it is necessarily an increase in the number of different elements.Inmost cases, the elements interact with each other in some()fashion, and thecomplexity of the whole increases much more than linearly.
The complexity of software is a(an) ()property, not an accidental one.Hencedescriptions of a software entity that abstract away its complexity often abstract away itsessence.Mathematics and the physical sciences made great strides for three centuries byconstructing simplified models of complex phenomena, deriving, properties from the models,and verifying those properties experimentally.This worked because the complexities()in the models were not the essential properties of the phenomena.It does not work when thecomplexities are the essence.
Many of the classical problems of developing software products derive from thisessential complexity and its nonlinear increases with size.Not only technical problems butmanagement problems as well come from the complexity.
问题1选项
E-mail地址由分隔符“()”分为前后两部分,分别指明用户名及邮件
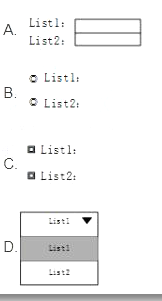
某 html 文档中有如下代码,则在浏览器中打开该文档时显示为( )。
<form>
Listl:
<input type="text" name="List1" />
<br / >
List2:
<input type="text" name="List 2 " />
< /form>
设有商品关系P(商品名,条形码,供应商号,价格,数量), “条形码”唯一标识关系P中的每一个元组,商品名不能为空,供应商号是关系P的外键。另有供应商关系S(供应商号,供应商名,地址,电话)。关系 P 中的商品名是唯一的。建立商品关系 P 的 SQL语句如下所示:
CREATE TABLE P( 商品名CHAR(30)( ),
条形码CHAR(30) ( ) ,
供应商号 CHAR(5) ,
价格 CHAR(20) ,
数量CHAR(20)
( )(供应商号) REFERENCES S(供应商号));
查询供应商及价格小于等于 2500 元且大于等于 1280 元的“电冰箱”的数量的SQL语句为:
SELECT商品名,供应商名,价格,数量
FROM P
WHERE商品名= ’电冰箱’ AND ( ) ;
将供应商号“12021”所供应的商品价格上涨3%的SQL语句为:
UPDATE P
( )
WHERE 供应商号= ’12021’;
查询供应商地址包含“西安”的供应商名及电话的SQL语句为:
SELECT供应商名,电话
FROM S
WHERE ( );
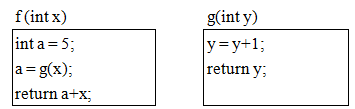
函数f()、g()的定义如下所示。已知调用f时传递给其形参x的值是1,若以传值方式调用g,则函数f的返回值为( );若以传引用方式调用g,则函数f的返回值为( )。